Types of Hydroponic Systems
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic systems allow for soil-free plant growth using nutrient-rich water.
- There are several types of hydroponic systems, each with its own advantages and applications.
- Common systems include NFT, DWC, Ebb and Flow, and Aeroponics.
- Understanding the different systems can help you choose the best setup for your gardening needs.
Hydroponic gardening is revolutionizing the way we grow plants, offering a soil-free method that maximizes efficiency and yields. This article explores the different types of hydroponic systems available, their applications, and how they can benefit your gardening efforts. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced gardener, understanding these systems will help you make informed decisions for your hydroponic setup.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution to provide all necessary nutrients directly to the roots. This innovative approach is ideal for urban settings, small spaces, and areas with poor soil quality. The result is faster growth rates, higher yields, and the ability to grow crops year-round.
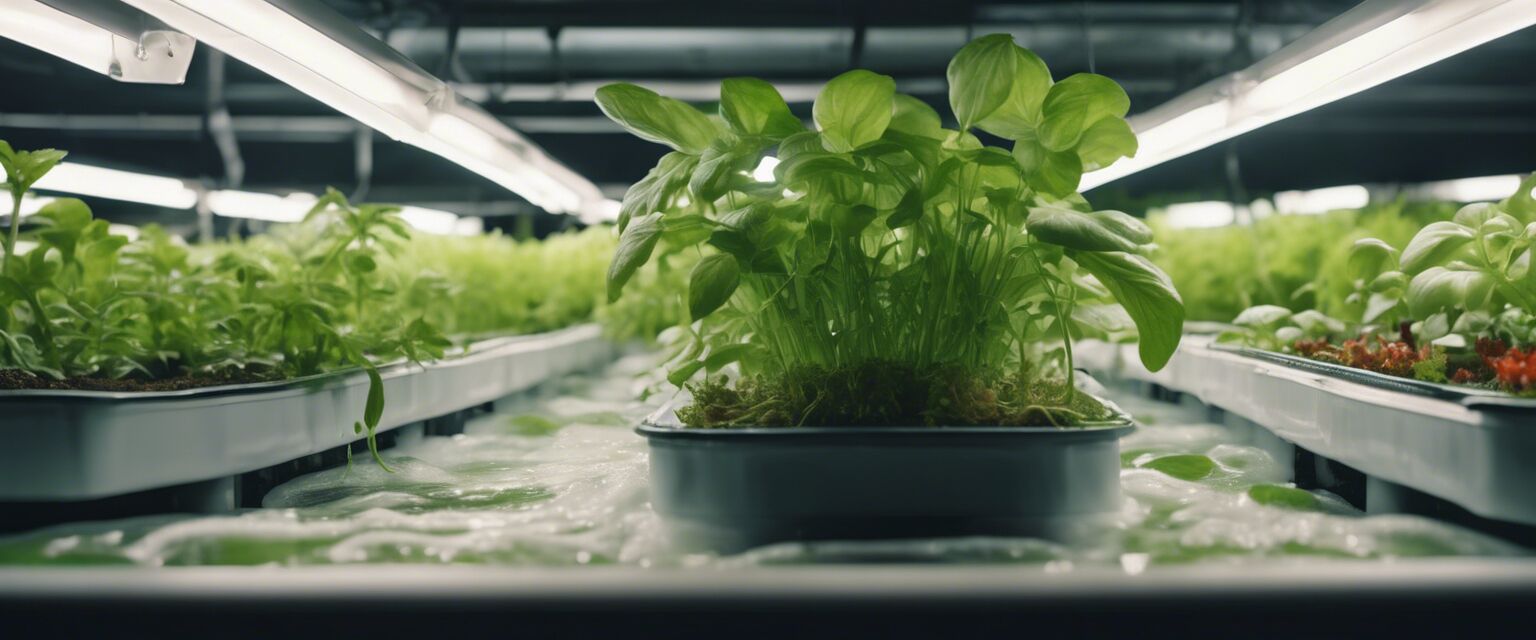
Types of Hydroponic Systems
There are several types of hydroponic systems, each designed to cater to different types of plants, growth conditions, and user preferences. Below, we outline the most common hydroponic systems:
| Type of System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) | Efficient nutrient use, low water consumption | Requires careful monitoring, risk of pump failure |
| Deep Water Culture (DWC) | Simple design, roots submerged in nutrient solution | Oxygen management is crucial, potential for root rot |
| Ebb and Flow | Flexibility in growing conditions, suitable for various plants | Complex setup, requires pump and timer |
| Aeroponics | High oxygen levels for roots, efficient nutrient delivery | Requires precise misting, more advanced technology |
| Wick System | Simple and passive, no pumps needed | Limited to smaller plants, slower growth rates |
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a hydroponic system where a thin film of nutrient solution flows over the roots of the plants. This method is highly efficient in its use of water and nutrients, making it a popular choice for growers looking to maximize their resources.
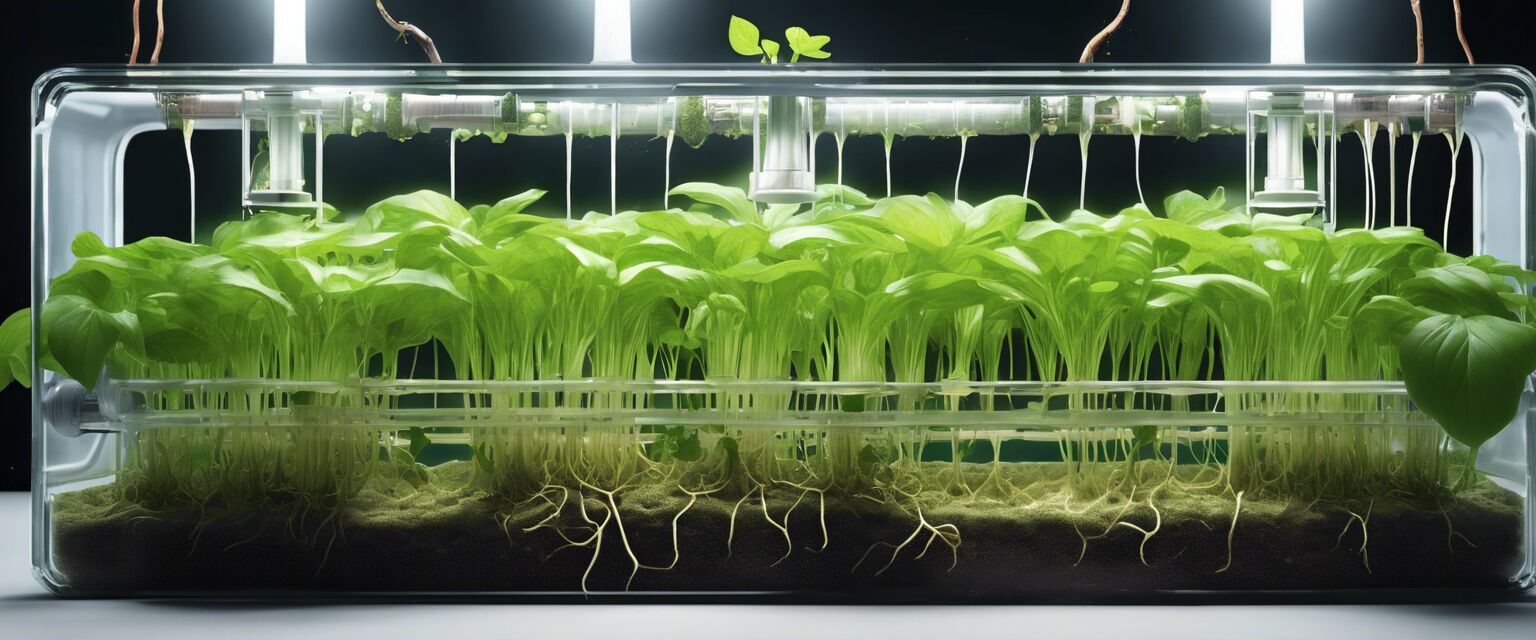

Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture is one of the simplest hydroponic systems, where plant roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich oxygenated water solution. This method is highly effective and allows for vigorous growth.

Ebb and Flow System
The Ebb and Flow system, also known as Flood and Drain, periodically floods the grow bed with nutrient solution and then drains it back into a reservoir. This system works well for a variety of plants and can accommodate larger setups.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a cutting-edge technique where plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solution. This method provides high oxygen levels to the roots and can lead to rapid growth rates.
Wick System
The Wick System is a passive hydroponic method that uses a wick to draw nutrient solution up to the plant roots. This is one of the easiest systems to set up but is generally limited to smaller plants.
Pros
- Efficient use of water and nutrients
- Faster growth rates compared to soil gardening
- Ability to grow food year-round
- Less space required for gardening
Cons
- Higher initial setup cost
- Requires careful monitoring of nutrient levels
- Potential for system failures
- Learning curve for beginners
Applications of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems can be used for a variety of applications:
- Home Gardening: Ideal for growing fresh herbs and vegetables in small spaces.
- Commercial Production: Large-scale setups can produce high yields for sale in markets.
- Research: Used in agricultural research to study plant growth and nutrient uptake.
- Education: Schools and universities use hydroponics to teach students about sustainable agriculture.
Choosing the Right Hydroponic System
Choosing the right hydroponic system depends on several factors, including:
- Your available space and setup.
- The types of plants you wish to grow.
- Your budget and willingness to invest in equipment.
- The amount of time you can dedicate to monitoring and maintaining the system.
Conclusion
Hydroponic gardening systems offer a revolutionary way to grow plants without soil, catering to urban gardeners and commercial producers alike. From NFT to aeroponics, each system has unique advantages and disadvantages. By understanding these systems and their applications, you can make informed choices and enjoy the benefits of hydroponic gardening.
Tips for Beginners
- Start with a simple system like DWC or Wick System before moving to more complex setups.
- Invest in quality nutrient solutions to ensure healthy plant growth.
- Regularly monitor pH and nutrient levels for optimal results.
- Research the specific needs of the plants you wish to grow.
Further Reading
For more information on hydroponic gardening, check out our other articles:
- Grow Lights - Essential for optimal plant growth.
- Growing Media - Options for supporting your plants.
- Hydroponic Systems - Explore various hydroponic products.
- Monitoring & Sensors - Tools to track your garden's health.
- Nutrient Solutions - Key to feeding your plants.