Hydroponic Systems for Educational Purposes
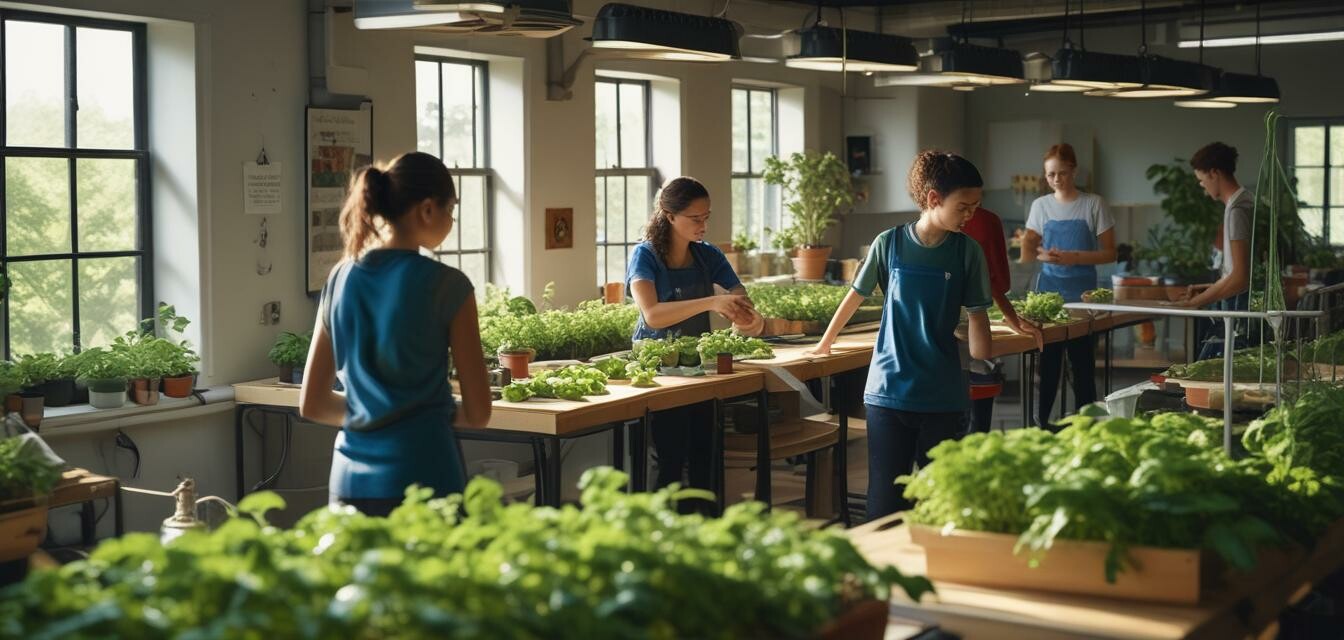
- Hydroponic systems offer a hands-on approach to learning about biology, sustainability, and food production.
- Implementing these systems can engage students and bolster their understanding of environmental sciences.
- Creating a hydroponic setup in the classroom can be done with minimal resources and space.
- There are various types of hydroponic systems suitable for educational environments, from simple DIY methods to more complex setups.
As educators increasingly look for innovative ways to engage students in learning about sustainability, biology, and food production, hydroponic systems have emerged as a powerful teaching tool. These soil-less growing systems not only provide students with hands-on experiences but also foster discussions about critical topics such as resource management and environmental stewardship. This guide will outline how to effectively implement hydroponic systems in classrooms, offering both practical tips and educational benefits.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, utilizing nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver all essential nutrients directly to plant roots. This technique offers a variety of advantages, including:
- Faster plant growth rates
- Higher yields compared to traditional soil gardening
- Reduced water usage
- Year-round cultivation, regardless of climate
Benefits of Hydroponic Systems in Education
Implementing hydroponic systems in educational settings can significantly enhance student learning experiences. Here are some notable benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Hands-On Learning | Allows students to directly participate in growing plants, making learning engaging and interactive. |
| Real-World Applications | Encourages discussions about sustainability, nutrition, and agricultural technology. |
| Engagement with Science | Facilitates environmental studies, botany, and ecology lessons through practical applications. |
| Adaptability | Can be tailored to fit various classroom sizes, age groups, and subject focuses. |
Types of Hydroponic Systems Suitable for Classrooms
When choosing a hydroponic system for educational purposes, consider the following popular types:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A shallow stream of nutrient solution flows through channels where plants are rooted.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants are suspended in nutrient solution, with air stones providing oxygen.
- Wicking System: Uses a wick to draw nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant roots.
- Drip System: Nutrient solution is dripped directly onto the plant roots at scheduled intervals.
- Vertical Hydroponics: Stack layers of growing systems to maximize space, ideal for smaller classrooms.
Implementing Hydroponic Systems in the Classroom
Follow these steps to implement a hydroponic system in your classroom:
- Choose the right system: Select a hydroponic system that fits your classroom size and budget.
- Gather materials: Collect necessary materials such as containers, grow lights, and nutrient solutions.
- Engage students: Involve students in the setup and explain each step of the process.
- Monitor plants: Teach students to observe plant growth and nutrient levels, encouraging critical thinking.
- Document progress: Keep journals or digital records of plant growth and lessons learned.
Learning Opportunities and Curriculum Integration
Hydroponic systems can be incorporated into a variety of subjects, offering unique learning opportunities:
- Science: Study plant biology, ecosystems, and environmental science.
- Mathematics: Measure growth rates, calculate nutrient ratios, and analyze data.
- Health: Discuss the importance of nutrition and sustainable food production.
- Technology: Explore automated watering systems and sensors used in commercial hydroponics.
For more classroom project ideas, check out our DIY Projects section where educators can find creative ways to enhance their hydroponic experience.
Key Considerations for Educators
While setting up hydroponic systems is exciting, educators should also keep the following considerations in mind:
- Ensure proper maintenance of the system to avoid issues with plant health.
- Incorporate safety measures to handle electrical components and nutrient solutions.
- Be prepared for lessons in troubleshooting common issues.
- Encourage teamwork and collaboration among students for a more enriching experience.
Conclusion
Implementing hydroponic systems in classrooms can provide students with invaluable knowledge in sustainable practices and food production. As educators, we have the unique opportunity to engage students in meaningful conversations about our environment and food systems through this innovative gardening approach. By introducing hydroponics into your educational curriculum, you can inspire students to think critically about their role in sustainability.
Pros
- Enhances student engagement through hands-on learning.
- Promotes discussions about sustainability and environmental science.
- Flexible and customizable to fit different educational needs.
- Encourages collaboration and teamwork among students.
Cons
- Requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
- Initial setup costs can vary based on system type.
- Potential technical challenges that may arise for educators.
- Resource intensive, depending on plant variety and system complexity.
For further reading on hydroponic gardening, you might also find interest in our articles about Hydroponic Systems and Nutrient Solutions to enhance your understanding and improve educational projects.