The Future of Hydroponic Education
Key takeaways
- Hydroponics is increasingly featured in educational institutions for practical learning and sustainability.
- Hands-on experience in hydroponic systems enhances students' understanding of sustainable agriculture.
- Integration of hydroponics aligns with global trends in food production and urban farming.
- Hydroponic gardening can improve curriculum engagement, encouraging interest in STEM fields.
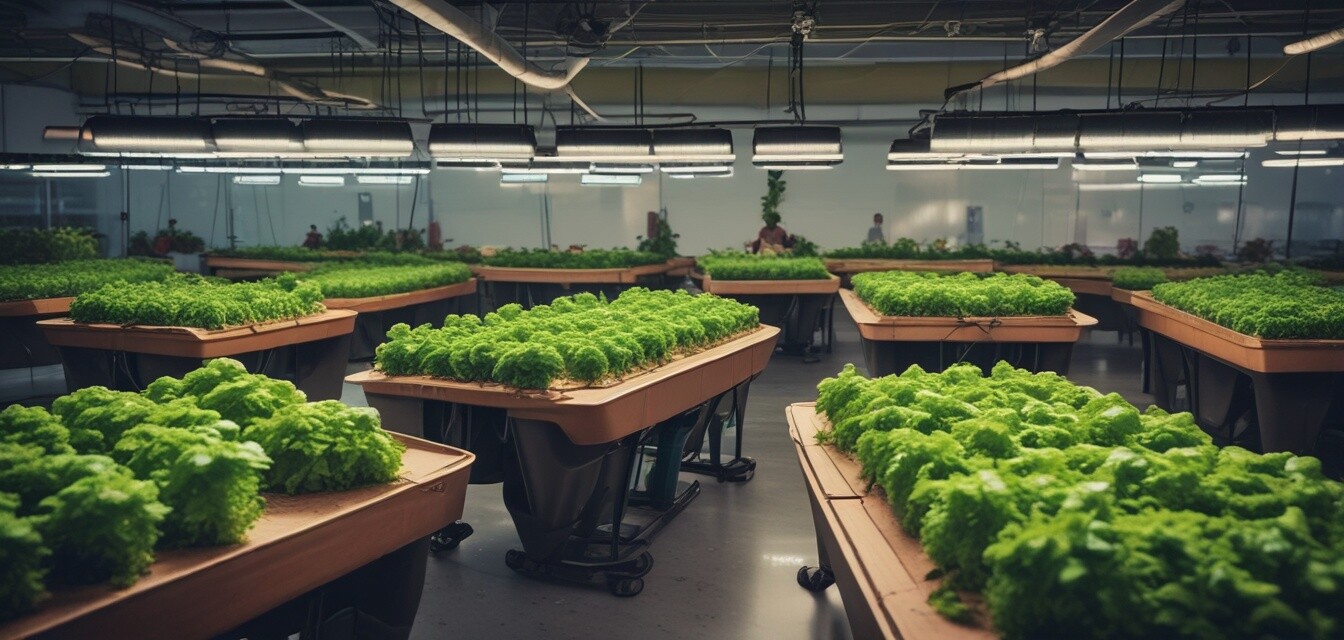
As the world turns its attention towards sustainable agriculture, hydroponic gardening is becoming an essential subject within various educational institutions. This approach offers practical hands-on experiences that not only engage students but also promote sustainable practices in agriculture. This article delves into how hydroponic education is evolving and why it is beneficial for both students and the environment.
Growing interest in hydroponic education
Educational institutions are beginning to recognize the importance of integrating hydroponics in their curriculums. With the rise of urban farming and the need for sustainable food production methods, schools and universities are choosing hydroponic systems as a key component of their teaching. This trend reflects a broader shift towards embracing environmentally-friendly practices in agriculture, aligning with modern educational imperatives.
Benefits of hands-on learning
Hands-on learning offers several advantages in the context of hydroponic education, including:
- Real-time experience with nutrient solutions and plant growth.
- Improved engagement through active participation in the learning process.
- Understanding complex scientific principles, including biology and chemistry.
- Development of problem-solving skills and critical thinking.
Implementing hydroponic systems in school curriculums
Adopting hydroponics in educational settings involves several steps. Educators must create a curriculum that integrates hydroponic gardening into various subjects. Here is a general outline of the implementation process:
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Assess resources | Evaluate available space, funding, and materials needed for hydroponic systems. |
| 2. Develop curriculum | Create lesson plans that incorporate hydroponics into science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects. |
| 3. Build hydroponic setups | Construct hydroponic systems—this could be indoor or outdoor depending on the school's location. |
| 4. Educate staff and students | Provide training to teachers and students regarding hydroponic methods and maintenance. |
| 5. Launch programs | Start hands-on projects and encourage students to engage with the hydroponic systems. |
Future trends in hydroponic education
As technology advances, the future of hydroponic education looks promising. Several trends are emerging that are set to influence educational practices:
- Incorporation of technology: Smart sensors and automated systems are transforming how hydroponic gardens are maintained, allowing for more sophisticated learning experiences.
- Online education: Virtual hydroponic simulations and online courses will make it easier for students to learn about hydroponics without needing physical resources.
- Collaboration with communities: Partnerships between schools and local farms will help integrate real-world experiences into the hydroponic curriculum, enhancing community engagement.
Impact on students and the community
The impact of implementing hydroponic education is far-reaching. By hands-on experience, students not only gain valuable agricultural skills but also a deeper understanding of sustainability. The community benefits as well; educational institutions can become local hubs for knowledge sharing, promoting sustainable food practices and inspiring future generations of eco-conscious citizens.
Pros
- Interactive learning experience for students.
- Encourages interest in career opportunities in agriculture and environmental science.
- Promotes sustainable practices and environmental stewardship.
Cons
- Initial costs for setting up hydroponic systems can be high.
- Requires ongoing maintenance and education to properly operate.
- Limited understanding of hydroponic systems in some educational staff.
Conclusion
The integration of hydroponic gardening within educational institutions signifies a step forward for sustainable agriculture. As students engage with this innovative form of learning, they not only gain practical skills but also contribute to a greener future. The benefits of incorporating hands-on experiences in hydroponic education extend beyond the classroom, influencing communities and preparing the next generation for challenges in food production and environmental stewardship.
For more insights into hydroponic systems, visit our Hydroponic Systems page. Explore buying guides to learn more about hydroponic equipment and nutrient solutions essential for your garden. Stay updated with our News and Trends section for the latest innovations in hydroponics.