Hydroponic Farming and its Role in Food Security
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic farming is a method that allows for soil-less crop production, offering numerous benefits in urban settings.
- This technique can contribute significantly to food security by providing fresh produce in areas with limited agricultural space.
- Community-driven hydroponic projects demonstrate the potential for enhancing food accessibility and education.
- By utilizing modern technologies, hydroponic systems can increase yield efficiency while reducing water usage.
- Collaborative urban agriculture initiatives can promote a sustainable future and empower local communities.
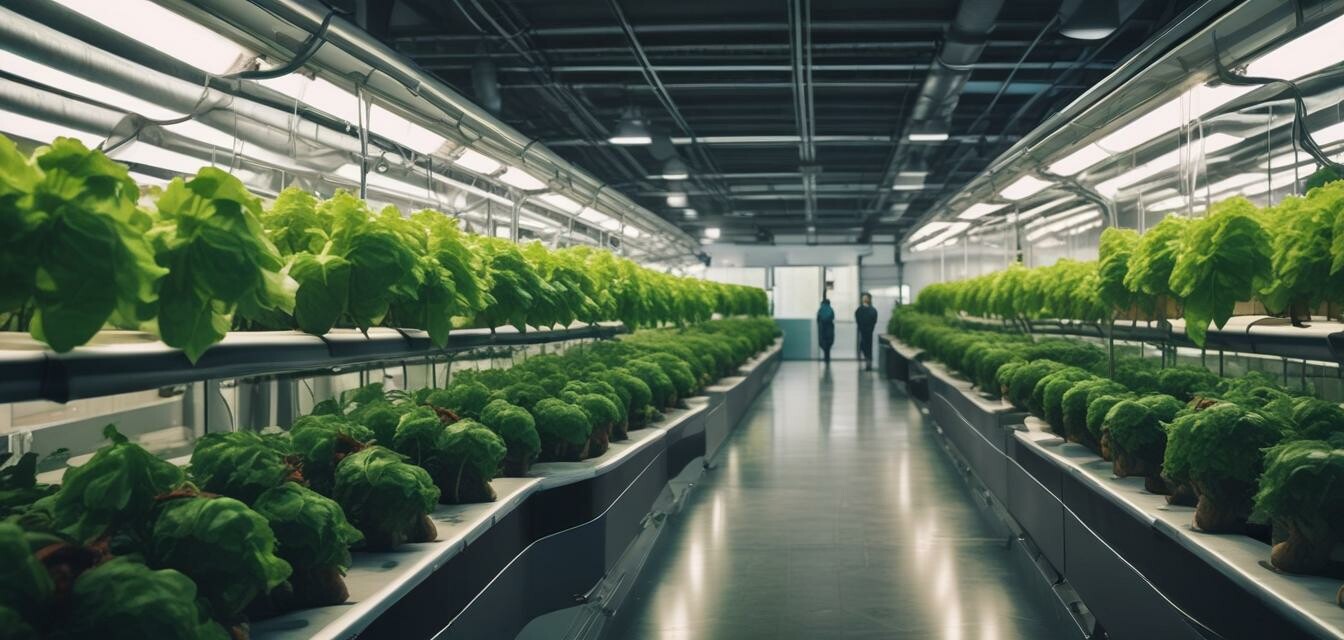
In recent years, hydroponic farming has emerged as a viable solution to address global food security challenges. This innovative approach to agriculture allows for the cultivation of plants without soil, utilizing a nutrient-rich water solution instead. As urban areas continue to grow and arable land becomes limited, hydroponics offers an effective way to produce fresh food closer to consumption sites, thereby improving access to healthy food.
What is Hydroponic Farming?
Hydroponic farming is a method of growing plants in a controlled environment, using nutrient solutions delivered directly to the roots. It eliminates the need for soil and maximizes space usage, making it particularly suited for urban environments. Hydroponics can support various types of crops including vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
Advantages of Hydroponic Farming
- Space efficiency: Hydroponic systems can be set up vertically, allowing for higher yields in smaller spaces.
- Water conservation: This method uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming.
- Faster growth rates: Plants can grow more quickly due to optimized nutrient delivery.
- Reduced pesticide use: Controlled environments mean fewer pests and diseases, minimizing the need for chemical treatments.
The Impact of Hydroponics on Food Security
With the global population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, food security has become a pressing challenge. Hydroponic farming can play a pivotal role in ensuring a reliable food supply through the following means:
1. Urban agriculture initiatives
Many cities are now adopting hydroponic farming as part of their urban agriculture strategies. With fresh produce grown on rooftops or vacant lots, urbanites can access food that is both healthy and locally sourced.
2. Community projects
Community-driven hydroponic projects are becoming increasingly popular. These initiatives not only provide food but also educate residents on sustainable practices, creating a sense of community ownership over food production.
3. Responsive food production systems
Hydroponics allows for rapid response to food shortages during crises, such as natural disasters or pandemics. By establishing local hydroponic farms, communities can maintain food production even when traditional supply chains are disrupted.
Case Studies of Successful Hydroponic Initiatives
Let's look at some successful examples showcasing how hydroponic farming has positively influenced local food security:
| Project Name | Location | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brooklyn Grange | New York City, USA | A rooftop farm that demonstrates sustainable urban agriculture. | Provides fresh produce to local markets and restaurants. |
| Urban Farming | Detroit, USA | Community farms utilizing hydroponic systems to revitalize urban spaces. | Improved access to healthy food in food deserts. |
| Sky Greens | Singapore | The world’s first vertical farm employing a hydraulic system. | Reduces food imports and cultivates fresh crops sustainably. |
Challenges and Limitations of Hydroponic Farming
While hydroponic farming offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges:
- Initial investment: Startup costs for equipment and infrastructure can be high, which may deter some growers.
- Technical expertise: Hydroponics requires knowledge in both plant biology and technology.
- Energy consumption: Some systems rely heavily on electricity for lighting and temperature control, which might not be sustainable in all areas.
Pros
- Efficient use of space and resources.
- Can be set up in a variety of environments.
- Supports year-round food production.
Cons
- Higher upfront costs and ongoing operational costs.
- Requires continuous monitoring and maintenance.
- Potential technical failures if not managed well.
The Future of Hydroponic Farming
As technology advances, the future of hydroponic farming looks bright. Innovations such as automated monitoring systems, enhanced nutrient solutions, and improved growing media will likely increase efficiency and lower costs.
Conclusion
Hydroponic farming represents a sustainable solution to many challenges associated with food security, particularly in urban environments. By investing in technology and fostering community effort, we can ensure that healthy food is accessible to all, paving the way for a promising future in agriculture.
Learn More
Explore our buying guides for tips on setting up your own hydroponic farm, or read about the latest news and trends in the hydroponic industry to stay informed. For those interested in community-driven solutions, check out our insights on DIY projects that can aid in food production.