Hydroponics in Education: Growing Knowledge
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic gardening integrates sustainable practices into educational programs.
- Hands-on learning with hydroponics boosts student engagement and interest in agriculture.
- Hydroponics fosters essential skills such as research, planning, and teamwork.
- Various schools and community centers have successfully implemented hydroponic curricula.
- This innovative approach to learning prepares students for future careers in the agricultural sector.
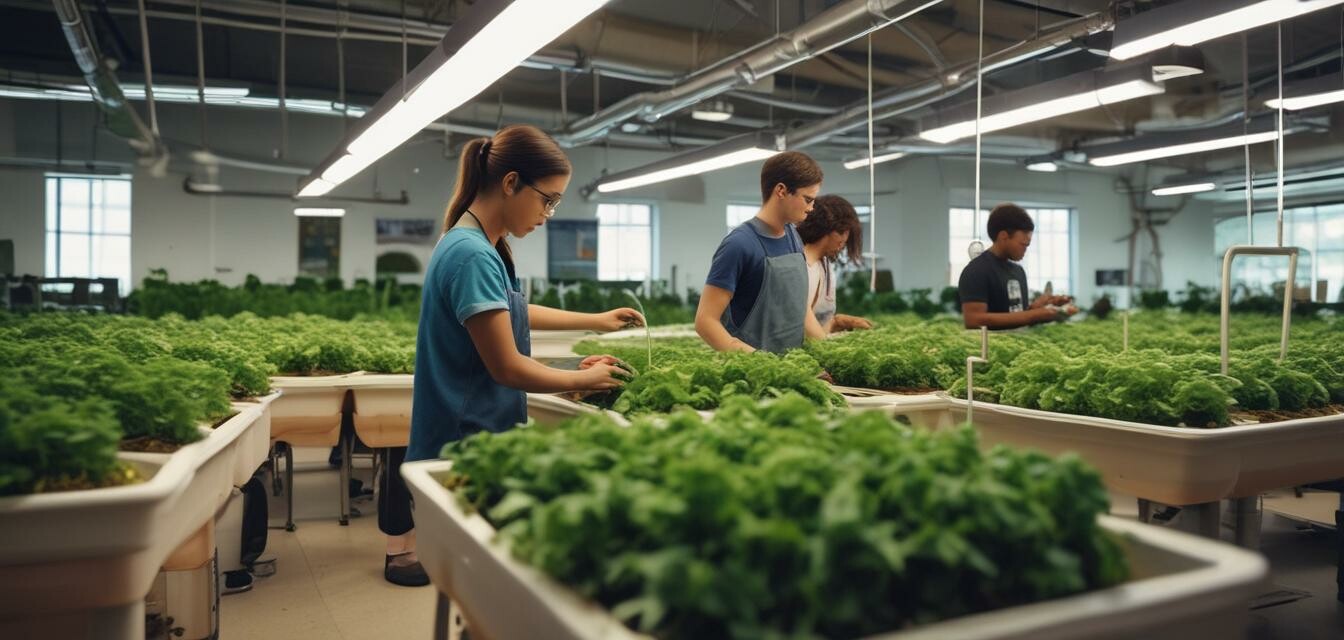
As sustainability takes center stage in conversations around education and agriculture, hydroponic gardening has emerged as a practical tool for teaching the next generation. This method of soil-less farming not only provides students with essential skills but also ignites their passion for growing food and caring for the environment.
The role of hydroponics in education
Hydroponics allows educators to teach students about sustainable practices in a hands-on way. Many programs have begun to integrate this innovative gardening method into their curricula, engaging young minds in the science of agriculture without the limitations of traditional soil-based gardening.
Benefits of using hydroponics in schools
- Hands-on learning: Students can easily monitor growth and understand plant biology.
- Safe and efficient: Hydroponics can be practiced indoors, reducing the need for outdoor space.
- Interdisciplinary learning: Hydroponic gardening incorporates science, math, and environmental studies.
- Modern technology: Students learn about monitoring systems and nutrient solutions.
Programs and initiatives
Across the globe, various programs are adopting hydroponics as an educational tool. Some notable examples include:
| Program Name | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Agriculture Initiative | New York City, USA | Teaches inner-city youth about sustainable food production through hydroponic gardens. |
| Soil-less Science | California, USA | Integrates hydroponics into science curricula, offering hands-on experiences for students. |
| Aquaponic Learning | Sydney, Australia | Combines hydroponics with aquaculture to teach about ecosystems and sustainability. |
Case studies
Several educational institutions have reported positive outcomes from implementing hydroponic gardening projects:
- High School Hydroponics Project: A high school in Texas encouraged students to create their own hydroponic systems, leading to increased interest in agricultural science.
- Community Garden Program: A community center in Michigan involved local students in maintaining a hydroponic garden, fostering teamwork and community spirit.
How hydroponics prepares students for the future
Education through hydroponics is not just about planting seeds; it is about planting the seeds of knowledge and responsibility. Students learn vital skills that can be applied in various career paths, including:
- Agronomist
- Environmental Scientist
- Food Safety Specialist
- Urban Planner
Challenges and considerations
Implementing hydroponics in educational settings isn't without its challenges. Here are some key considerations:
Pros
- Engages students in practical and relevant learning experiences.
- Promotes environmental awareness and sustainability.
- Fosters teamwork and collaboration among students.
Cons
- Initial setup costs can be high for schools.
- Maintenance and monitoring require ongoing commitment.
- Not all curricula may be compatible with hydroponic integration.
Conclusion
Hydroponic gardening in education is a powerful tool that cultivates not only plants but also a deeper understanding of sustainable practices among students. As technology and environmental concerns continue to evolve, integrating hydroponics into educational systems will likely produce the next generation of environmentally-conscious farmers and innovators.
Tips for Starting Hydroponics in Education
- Start small with basic hydroponic systems.
- Incorporate lessons on plant biology and ecosystems.
- Encourage creativity—let students design their own systems.
For more information on useful hydroponic systems, check out our various hydroponic systems and buying guides for educators and enthusiasts alike!