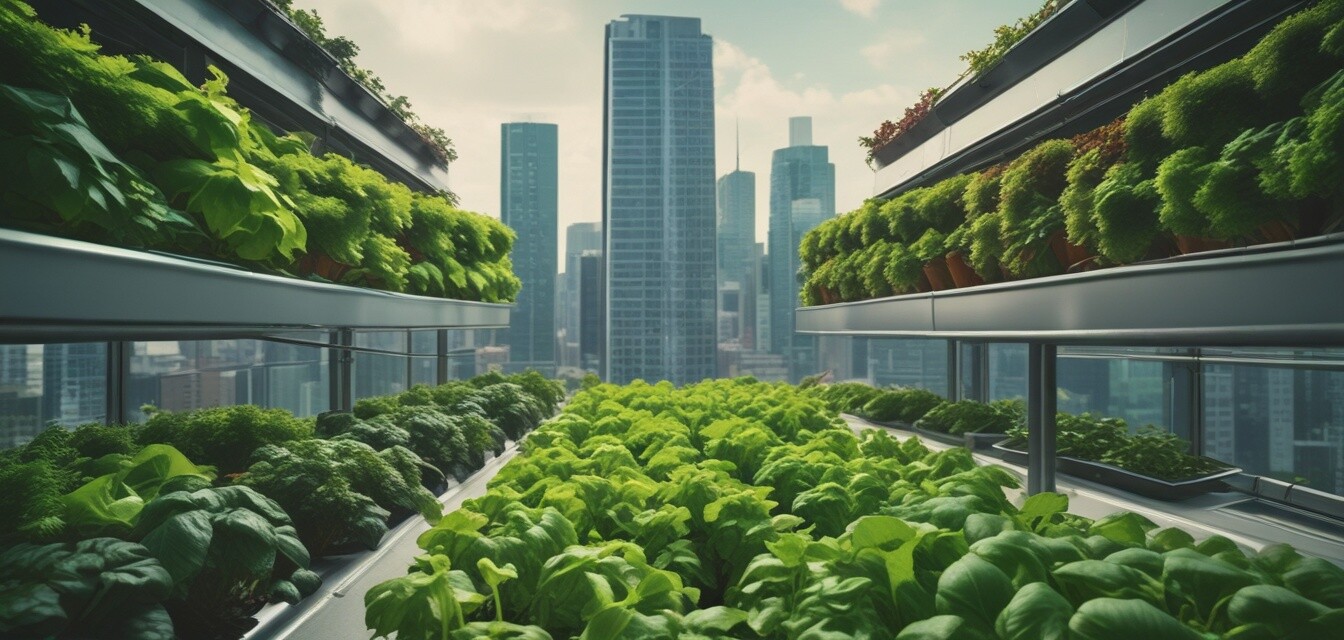
The connection between hydroponics and food equity
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics can provide consistent access to fresh produce in underserved areas.
- This method of farming reduces land usage and can be set up in urban environments.
- Hydroponic systems can contribute to local economies by creating jobs and sustainable practices.
- Investing in hydroponic systems can enhance community resilience against food shortages.
As the global population continues to grow, addressing food equity becomes increasingly crucial. Many underserved communities lack access to fresh fruits and vegetables, leading to health disparities and food insecurity. Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, offers innovative solutions to these challenges. This article explores how hydroponics can serve as a viable means to promote food equity, particularly in urban settings.
Understanding food equity
Food equity is defined as the fair distribution of healthy food for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location. Unfortunately, many communities, particularly in urban areas, experience food deserts characterized by limited access to fresh produce and healthy food options.
Root causes of food inequity
- Low income levels preventing the purchase of fresh produce.
- Lack of transportation to grocery stores with fresh food options.
- High prices of healthy food relative to processed alternatives.
- Insufficient knowledge about nutrition and cooking healthy meals.
How hydroponics comes into play
Hydroponics has the potential to transform food access in cities facing food inequity. By enabling the cultivation of fresh produce anywhere, this method of agriculture addresses many of the barriers that contribute to food deserts.
Benefits of hydroponic systems
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Space efficiency | Hydroponic systems can be set up vertically or in small spaces, maximizing production in urban areas. |
| Water conservation | Using up to 90% less water than traditional farming, hydroponics is a sustainable choice for water-scarce regions. |
| Faster growth rates | Plants grown hydroponically often have accelerated growth rates, allowing for more frequent harvesting. |
| Reduced pesticide use | Indoor hydroponic systems can minimize pest issues, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. |
| Year-round production | Hydroponics allows for growing fresh food throughout the year, independent of seasonal changes. |
Empowering communities
Implementing hydroponic gardens in underserved communities promotes self-reliance and food security. Local individuals can manage these gardens, bringing fresh produce directly to their neighborhoods.
Case studies: Success stories in food equity
Numerous initiatives have successfully integrated hydroponics into communities to address food equity challenges. Here are a few notable examples:
| Program | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| City Farm | Chicago, IL | Turned vacant lots into productive farms, providing fresh produce to local residents. |
| GrowNYC | New York, NY | Utilized hydroponic systems in schools to teach students about food and nutrition. |
| The Urban Farming Project | Detroit, MI | Empowered communities to grow their own food, enhancing access to fresh produce. |
The role of technology in hydroponics
Advancements in technology are making hydroponic systems more accessible and efficient. Innovations such as automated nutrient delivery systems and monitoring sensors enhance the effectiveness of hydroponics, leading to higher yields and lower energy consumption. For more on cutting-edge hydroponic technology, check out our section on monitoring and sensors.
Building a hydroponic garden: Steps to get started
Interested in starting your hydroponic garden? Here are some simple steps to guide you:
- Choose a suitable location: Look for a space with plenty of natural light or where you can install grow lights.
- Select your hydroponic system: Options include nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), or drip systems.
- Gather necessary supplies: Purchase seeds, nutrient solutions, growing media, and your hydroponic system.
- Monitor your garden: Regularly check on your plants’ growth, nutrient levels, and environmental conditions.
- Harvest your produce: Enjoy the fruits of your labor as you gather fresh dishes from your hydroponic garden!
Conclusion
The integration of hydroponic systems into underserved communities presents a unique opportunity to enhance food equity. By addressing barriers to fresh produce access and promoting local food growth, hydroponics can empower individuals, boost local economies, and cultivate healthier communities.
Pros
- Can be set up in small urban spaces.
- Requires less water than traditional agriculture.
- Provides fresh produce year-round.
- Enhances local economies.
Cons
- Initial setup cost may be high.
- Requires specific knowledge to manage systems.
Learn more about hydroponic gardening
If you want to dive deeper into hydroponics, check out our detailed guides on buying hydroponic systems or explore our resources on grow lights for optimal plant growth. Stay informed on the latest innovations in hydroponics by visiting our news and trends section.